Introduction:
Have you ever wondered what goes into the fish food you buy at the store? Many commercial options are packed with fillers and artificial ingredients that might not provide the best nutrition for your fish. Making homemade fish food is not only a cost-effective alternative but also a way to ensure your fish are getting the healthiest and freshest ingredients.
Whether you have tropical fish, goldfish, or a saltwater aquarium, crafting your own homemade fish food allows you to tailor it to their specific dietary needs. In this guide, we’ll show you how to create nutritious and balanced homemade fish food using simple, high-quality ingredients that your fish will love. Let’s dive into the world of DIY homemade fish food and keep your fish thriving! For more expert advice on aquarium care and nutrition, check out The Fish Site, a trusted resource for all things aquatic.
Why Choose Homemade Fish Food?

Homemade fish food is an excellent way to provide your aquatic pets with better nutrition, fewer fillers, and significant cost savings compared to store-bought varieties. Whether you’re crafting different types of homemade fish food to suit specific species or simply seeking a healthier alternative, making homemade fish food at home allows you to control the quality and nutritional value. Let’s explore why this approach is the best choice for your fish. For more details on creating specific types of homemade fish food, check out our guide on how to make live fish food at home.
Homemade fish food offers a host of benefits for aquarium enthusiasts who want to ensure their aquatic pets thrive in the best possible environment. Let’s explore why making homemade fish food at home is a worthwhile choice:
1. Benefits of Making Fish Food at Home
Making your own homemade fish food provides unparalleled control over the ingredients you use. By selecting high-quality, fresh components, you can create a diet that’s far healthier than many commercial options. Additionally, homemade fish food can significantly reduce costs over time, as bulk ingredients like vegetables, seafood, and gelatin are often more economical than prepackaged alternatives.
Other advantages include:
- The ability to incorporate organic and pesticide-free ingredients.
- Eliminating preservatives and artificial additives commonly found in commercial foods.
- Tailoring nutritional content to boost fish health, such as adding ingredients rich in Omega-3 fatty acids for vibrant coloration or proteins for growth.
For more guidance on creating nutrient-rich live fish food at home, explore our full guide on making live fish food.
2. Drawbacks of Commercial Fish Food
Many off-the-shelf fish foods are designed for convenience, but this often comes at a nutritional cost. Common issues include:
- The use of fillers like wheat or soy, which provide little nutritional value to fish.
- Low-quality protein sources that may not meet the dietary needs of specific species.
- Preservatives and artificial coloring agents that could potentially harm fish over time.
3. Customizing Fish Food for Specific Fish Types
One of the most compelling reasons to make homemade fish food at home is the opportunity to customize it for the unique needs of your aquatic pets. Every species has specific dietary requirements, and homemade fish food lets you tailor recipes accordingly:
- Freshwater Fish: These species often benefit from a mix of plant-based and protein-rich ingredients, such as spinach, peas, and brine shrimp.
- Saltwater Fish: Marine fish may require higher levels of protein and fats, as well as trace elements like iodine from seaweed or nori.
- Herbivores vs. Carnivores: Herbivorous fish need a diet rich in algae and vegetables, while carnivores thrive on meaty sources like fish, shrimp, or squid.
Homemade fish food is an excellent way to optimize your aquarium’s ecosystem, offering a healthier, more economical, and customizable alternative to commercial options. With a little effort, you can make food that meets the precise needs of your aquatic companions, ensuring they thrive under your care. For more tips on crafting live fish food, don’t miss our guide on how to make live fish food at home.miss our guide on how to make live fish food at home.of your aquatic companions, ensuring they thrive under your care.
Essential Ingredients for Homemade Fish Food
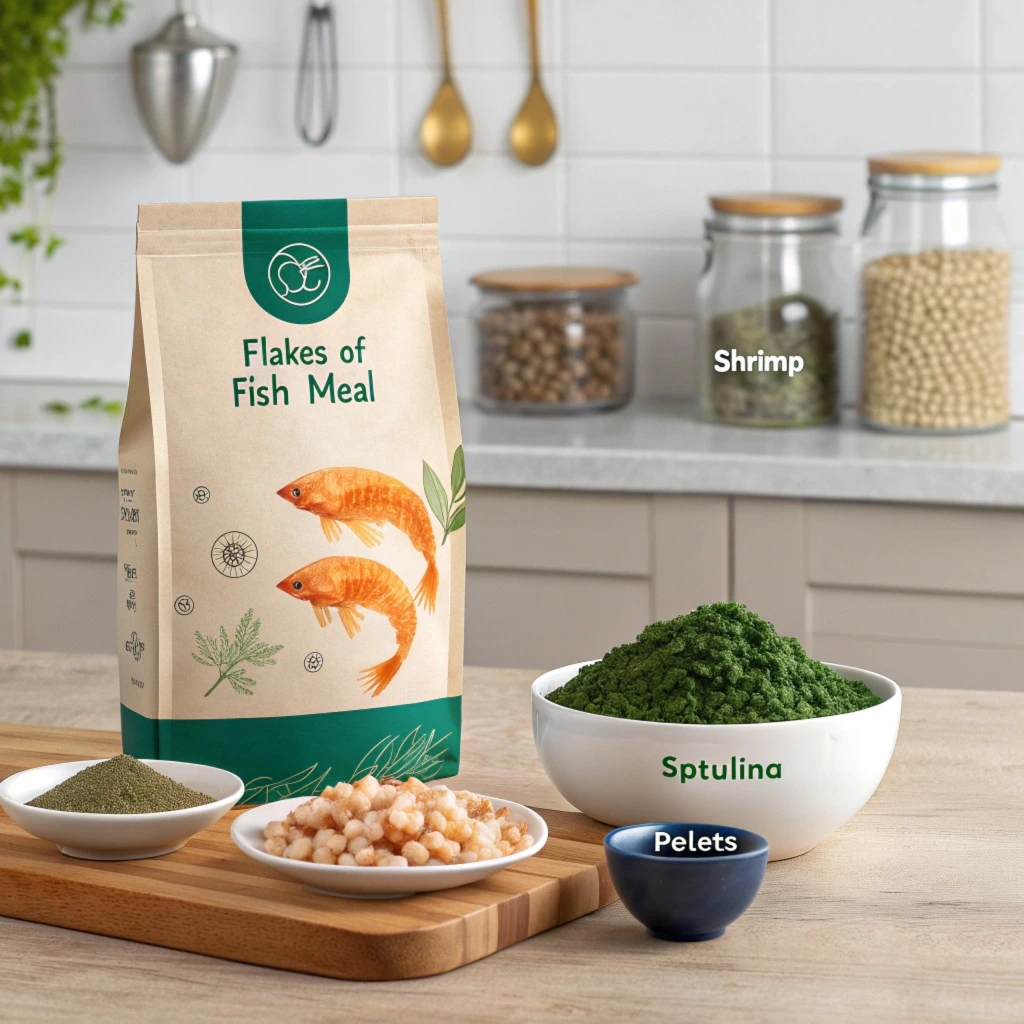

Discover the top ingredients to create nutritious homemade fish food, including shrimp, spirulina, and vegetables. Perfect for healthy, happy fish!
Creating nutritious, homemade fish food starts with understanding the dietary needs of your aquatic pets and selecting the best ingredients to meet those requirements. A well-rounded diet promotes growth, coloration, and overall health while ensuring your fish thrive in their environment.
1. Nutritional Needs of Fish: Proteins, Fats, and Vitamins
A balanced fish diet requires three key nutritional components:
Proteins: Essential for growth and development, proteins should make up a significant portion of your fish’s diet, especially for carnivorous and omnivorous species. Good protein sources include fish meal, shrimp, and other aquatic-based options.
Fats: Healthy fats provide energy and support various bodily functions, including the development of vibrant coloration. Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids, commonly found in seafood, are particularly important for many species.
Vitamins and Minerals: These are crucial for immune health and overall well-being. Ingredients like spirulina, vegetables, and certain fruits offer vitamins A, C, D, and E, as well as trace minerals like iodine and magnesium.
By balancing these components in your homemade fish food, you can ensure that your fish receive a complete and nutritious diet tailored to their species and lifestyle.
2. Best Ingredients for Homemade Fish Food
Choosing high-quality, nutrient-dense ingredients is the cornerstone of creating effective homemade fish food. Some of the best options include:
Shrimp: Packed with protein and fats, shrimp is an excellent ingredient for both freshwater and saltwater fish.
Spirulina: This blue-green algae is a powerhouse of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, promoting vibrant colors and supporting immune function.
Fish Meal: A concentrated protein source that mimics what fish eat in the wild, fish meal is ideal for most species.
Vegetables: Leafy greens like spinach and kale provide fiber and essential nutrients, while peas are excellent for preventing digestive issues such as bloating.
Seaweed or Nori: These are particularly beneficial for herbivorous and marine species, offering natural iodine and fiber.
3. Avoid Harmful Ingredients
While selecting ingredients, it’s equally important to know what to avoid. Some foods and additives can harm your fish or compromise the quality of their diet. Common pitfalls include:
Preservatives and Artificial Additives: These are often found in low-quality commercial fish foods and can be harmful over time. Stick to fresh, natural ingredients.
Over-Processed Foods: Ingredients like breadcrumbs or excessive starches can lead to poor water quality and may not provide sufficient nutritional value.
Toxic Ingredients: Avoid garlic in excess, as it can be harmful in large amounts. Similarly, avoid foods like citrus, which may alter the pH balance of your aquarium water.
Tips for Success
Blend and Freeze: After preparing your homemade fish food, blend it into a paste and freeze it into cubes for easy feeding.
Trial and Observation: Monitor your fish after introducing new food to ensure they are eating and thriving. Adjust the recipe as needed based on their response.
By focusing on the nutritional needs of your fish and using high-quality, safe ingredients, you can craft homemade fish food that supports their health and vitality. Not only will your fish benefit from this tailored approach, but you’ll also enjoy the satisfaction of seeing them flourish under your care., but you’ll also enjoy the satisfaction of seeing them flourish under your care.
Step-by-Step Guide to Making Fish Food
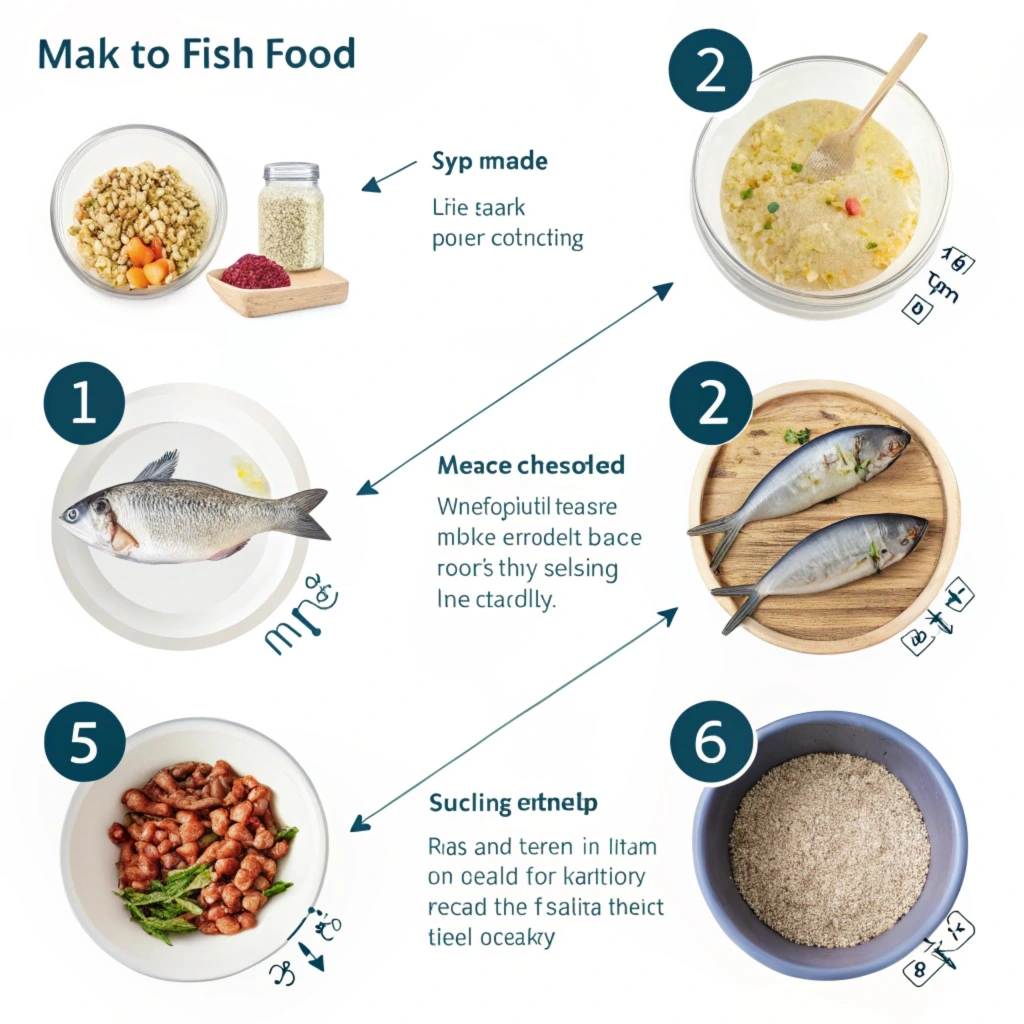
Learn how to prepare and store homemade fish food with this easy, step-by-step guide. From blending the base to shaping and freezing, it’s simple to do!
Making homemade fish food is a simple and rewarding process that allows you to customize your fish’s diet to meet their specific needs. Whether you’re preparing food for freshwater or saltwater fish, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the entire process—from gathering ingredients to storing your homemade food.
1. Preparing the Base
The first step in making fish food is to prepare the base, which will provide the essential nutrients your fish need. This typically involves blending key ingredients such as protein sources, vegetables, and a binding agent like gelatin to hold the mixture together. Here’s how to get started:
- Fish Meal or Shrimp: Start with a protein base like fish meal or finely chopped shrimp. These ingredients provide essential protein and fats, mimicking the natural diet of most fish.
- Vegetables: Choose nutrient-dense vegetables like peas, spinach, or carrots. These provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals. To ensure easy digestion for your fish, you may want to lightly steam the vegetables before blending them.
- Gelatin or Agar-Agar: This acts as a binder, helping the food hold its shape when dried or frozen. Dissolve the gelatin in water according to the package instructions, and then combine it with your protein and vegetable mix to form a paste. If you prefer a vegan alternative, agar-agar works well too.
Once all your ingredients are prepared, use a blender or food processor to mix them into a smooth, homogenous paste. The consistency should be thick enough to form into small pellets or wafers, but not too dry.
2. Mixing and Shaping the Food
Once the base is ready, it’s time to shape your homemade fish food. You have several options, depending on the type of food and how you want to serve it to your fish:
- Pellets: If you want to create small, bite-sized portions, roll the mixture into tiny pellets. You can make these by hand or use a rolling pin to flatten the paste and cut it into small pieces. You can also use a pellet-making machine if you want uniform, consistent sizes.
- Wafers: For larger fish or those that prefer bottom-feeding, shape the mixture into flat wafers. You can do this by spreading the mixture evenly on a baking sheet and then cutting it into squares or rectangles once it has set.
- Frozen Cubes: To create a convenient, long-lasting option, divide the mixture into small portions and freeze it in ice cube trays or silicone molds. This method is particularly useful for fish owners who want to feed their fish pre-portioned servings.
- Optional Add-ins: Depending on the species of fish, you can add special ingredients like spirulina, garlic, or fish oil to enhance the nutritional value and flavor.
3. Storing the Food
Proper storage is essential to maintaining the freshness and nutritional value of your homemade fish food. Depending on your preparation method, you can store the food in a few different ways:
- Freezing: The best way to store homemade fish food for long-term use is to freeze it. Frozen food retains its nutrients better and can be kept for up to 3-6 months. Simply place the food in airtight containers or freezer bags to prevent freezer burn and contamination.
- Refrigerating: If you plan to use the fish food within a few days, you can store it in the refrigerator. However, refrigerated food may not last as long as frozen food, so use it within 1-2 weeks for the best results.
- Storage Tips: To prevent contamination, ensure the food is stored in well-sealed containers to avoid exposure to moisture, which can promote bacterial growth. Label your containers with the date you prepared the food to keep track of freshness.
Making your own fish food is a straightforward process that only takes a little time and effort. By preparing a nutritious base, shaping the food into the preferred form, and storing it properly, you can ensure that your fish receive the best possible nutrition while saving money. Whether you choose to make pellets, wafers, or frozen cubes, homemade fish food is a great way to support the health of your aquarium inhabitants.
Types of Fish Food You Can Make at Home

Explore the variety of homemade fish food options, from live foods like brine shrimp to vegetable-based wafers and high-protein mixes for carnivorous fish.
When it comes to making homemade fish food, there are several types you can prepare based on the dietary needs of your aquarium inhabitants. Whether you have tropical fish, herbivores, or carnivores, you can create specialized foods that cater to their unique nutritional requirements. Let’s explore the different types of fish food you can make at home.
1. Live Food: Brine Shrimp, Daphnia (For Tropical Fish)
Live food is an excellent option for fish, particularly tropical species, that benefit from the natural proteins, fats, and vitamins found in live prey. It mimics what fish would encounter in the wild and can enhance the color and overall health of your pets.
- Brine Shrimp: These tiny, nutrient-packed crustaceans are a favorite for many tropical fish. They’re an excellent source of protein and Omega-3 fatty acids, which help promote vibrant coloration and improve fish health. You can easily hatch brine shrimp eggs at home using a simple aquarium setup, and they can be fed live to your fish or used to create freeze-dried or frozen food.
- Daphnia (Water Fleas): Daphnia are another form of live food that is particularly good for small fish and fry. These microscopic crustaceans are rich in essential fatty acids, amino acids, and fiber, making them a valuable addition to your fish’s diet. You can cultivate daphnia in a home aquarium or purchase them from live food suppliers to feed your fish fresh or freeze them for later use.
Live food is highly nutritious, but it can be more labor-intensive to maintain a culture. However, the benefits of feeding live prey to your fish, including encouraging natural hunting behaviors and boosting health, make it a worthwhile choice for enthusiasts.
2. Vegetable-Based Food: Spinach and Algae Wafers (For Herbivorous Fish)
Herbivorous fish thrive on plant-based diets, which are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Homemade vegetable-based fish food is a great way to ensure they receive a varied, healthy diet that supports digestion and long-term health.
- Spinach: A rich source of fiber, vitamins A, C, and K, as well as iron and calcium, spinach is an excellent ingredient for herbivorous fish. You can blend fresh spinach into your homemade fish food mixture, or you can blanch the leaves to make them easier for your fish to digest. Spinach also supports eye health and immune function.
- Algae Wafers: Algae wafers are a fantastic option for bottom-dwelling herbivorous fish, such as plecos, that enjoy grazing on natural food sources. You can make your own algae wafers by blending spirulina or other algae, along with gelatin or agar, to form a thick paste. Then, shape the paste into thin wafers and allow them to dry or freeze. Algae is rich in essential nutrients like iodine and Omega-3 fatty acids, supporting the overall health of your fish while also promoting vibrant colors.
For herbivorous fish, vegetable-based foods like spinach and algae provide the perfect combination of nutrients to meet their dietary needs. These foods are particularly helpful in preventing malnutrition and promoting good digestion.
3. High-Protein Food: Fish Meal and Shrimp Mix (For Carnivorous Fish)
Carnivorous fish have specific protein needs that must be met to ensure they thrive. Homemade high-protein fish food offers an excellent way to provide the necessary nutrients for these species, especially if you’re raising larger or more active fish that require more energy.
- Fish Meal: Made from ground-up fish, fish meal is a highly concentrated source of protein, making it an excellent base for a high-protein fish food mix. It contains essential amino acids, Omega-3 fatty acids, and other important nutrients that carnivorous fish need for muscle growth, tissue repair, and overall vitality.
- Shrimp: Shrimp is another great protein source for carnivorous fish. Rich in both protein and healthy fats, shrimp can be blended with fish meal to create a high-protein food that mimics the natural diet of many carnivorous species. Shrimp is also easy to digest and can improve fish coloration and overall health.
- Additional Protein Add-ins: You can also consider adding other protein-rich ingredients like krill, squid, or even small fish to your homemade mix, depending on the species of fish you’re feeding.
For carnivorous fish, a diet rich in high-quality protein helps ensure healthy growth, improves immune function, and enhances coloration. Blending fish meal and shrimp ensures that your fish get the balanced protein content they need without fillers or harmful additives.
By preparing different types of homemade fish food tailored to the dietary needs of your fish, you can ensure they receive the proper nutrients to thrive. Whether you opt for live food like brine shrimp and daphnia, vegetable-based foods like spinach and algae wafers, or high-protein options like fish meal and shrimp, homemade fish food allows you to provide your aquatic pets with the best possible nutrition. Not only will this improve their health and coloration, but it will also enrich their lives, as they enjoy a more varied and natural diet.
Conclusion
Making homemade fish food is a rewarding way to ensure your fish are getting the best possible care. By using fresh, high-quality ingredients and customizing the recipes to suit their dietary needs, you can promote healthier, more vibrant fish while saving money and reducing reliance on processed alternatives.
With just a little effort, you can provide a balanced and nutritious diet with homemade fish food that supports your fish’s growth, energy, and overall well-being. So why not give it a try? Your fish—and your wallet—will thank you!
Have you made your own homemade fish food before? Share your experience or tips in the comments below!

